Transformation Operators
map
根據資料轉型的函式,將 Observable 發出的資料做轉型
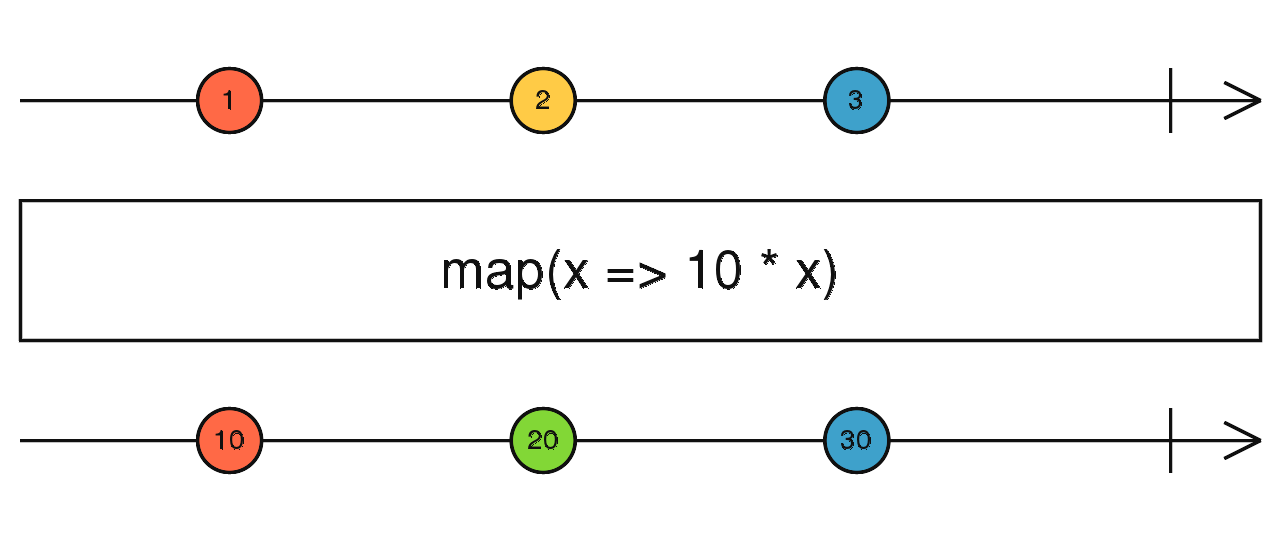
使用介面
map(project: function(value: T, index: number): R, thisArg: any): Observable<R>
使用範例
Observable.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
.map((value, idx) => {
return value * (idx % 2 == 0 ? 1 : 2);
})
.subscribe(value => console.log(value)); // 輸出: 1, 4, 3, 8, 5
※ map 是 RxJS 使用最頻繁之一的 operators
mapTo
送出一個固定的值
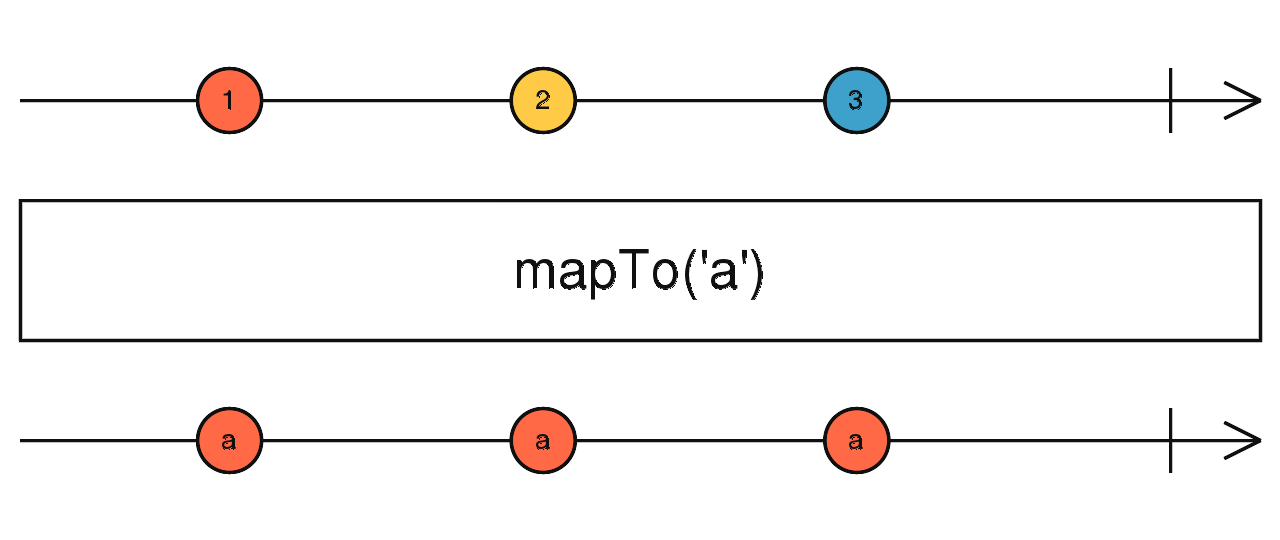
使用介面
mapTo(value: any): Observable
使用範例
Observable.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
.mapTo('Hi')
.subscribe(value => console.log(value)); // 輸出:Hi, Hi, Hi, Hi, Hi
concatMap
依序地結合兩個 Observable 發出的資料並做轉換
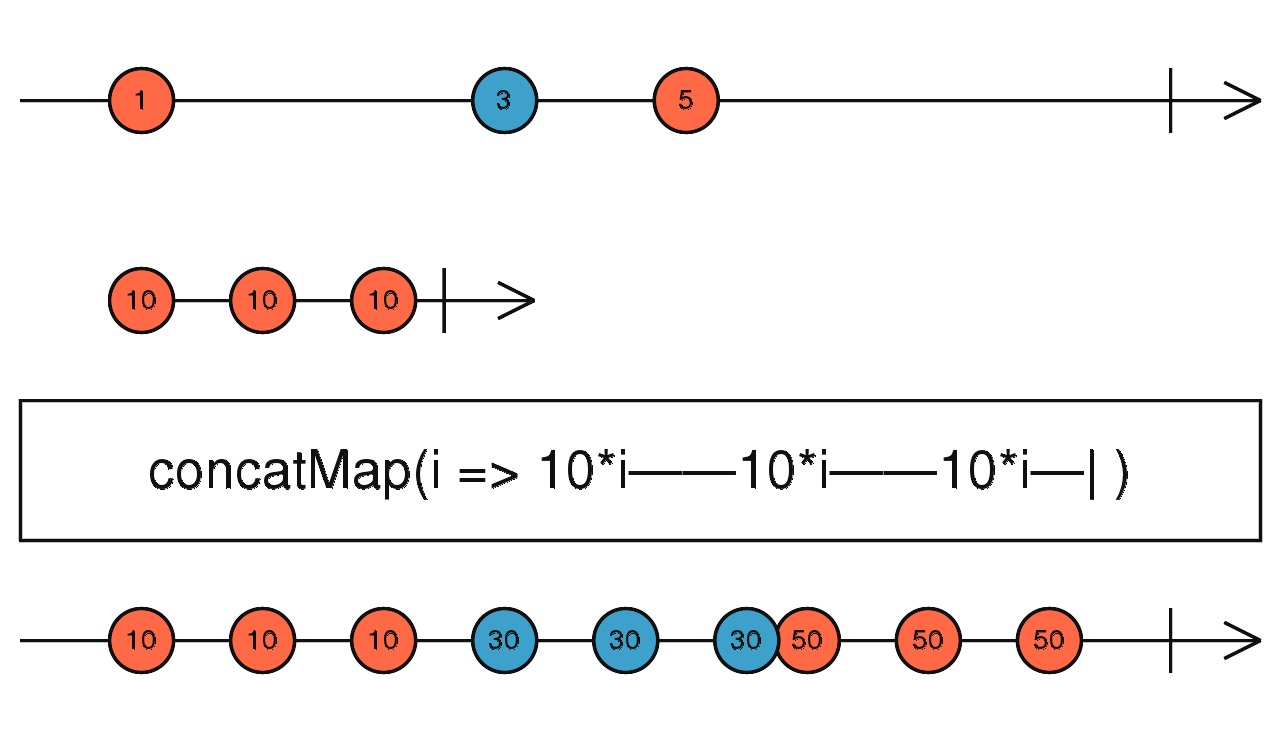
使用介面
concatMap(project: function(value: T, ?index: number): ObservableInput, resultSelector: function(outerValue: T, innerValue: I, outerIndex: number, innerIndex: number): any): Observable source
使用範例
Observable.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
.concatMap(
(value, idx) => {
const _v = value * (idx % 2 == 0 ? 1 : 2);
return Observable.of(_v);// 輸出:1, 4, 3, 8, 5
},
(outerValue, innerValue) => {
console.log({outValue, innerValue}); // 輸出:{1,1},{2,4},{3,3},{4,8},{5,5}
return outerValue * innerValue
})
.subscribe(value => console.log(value));// 輸出:1, 8, 9, 32, 25
concatMapTo
依序地結合兩個 Observable 並送出一個固定的值
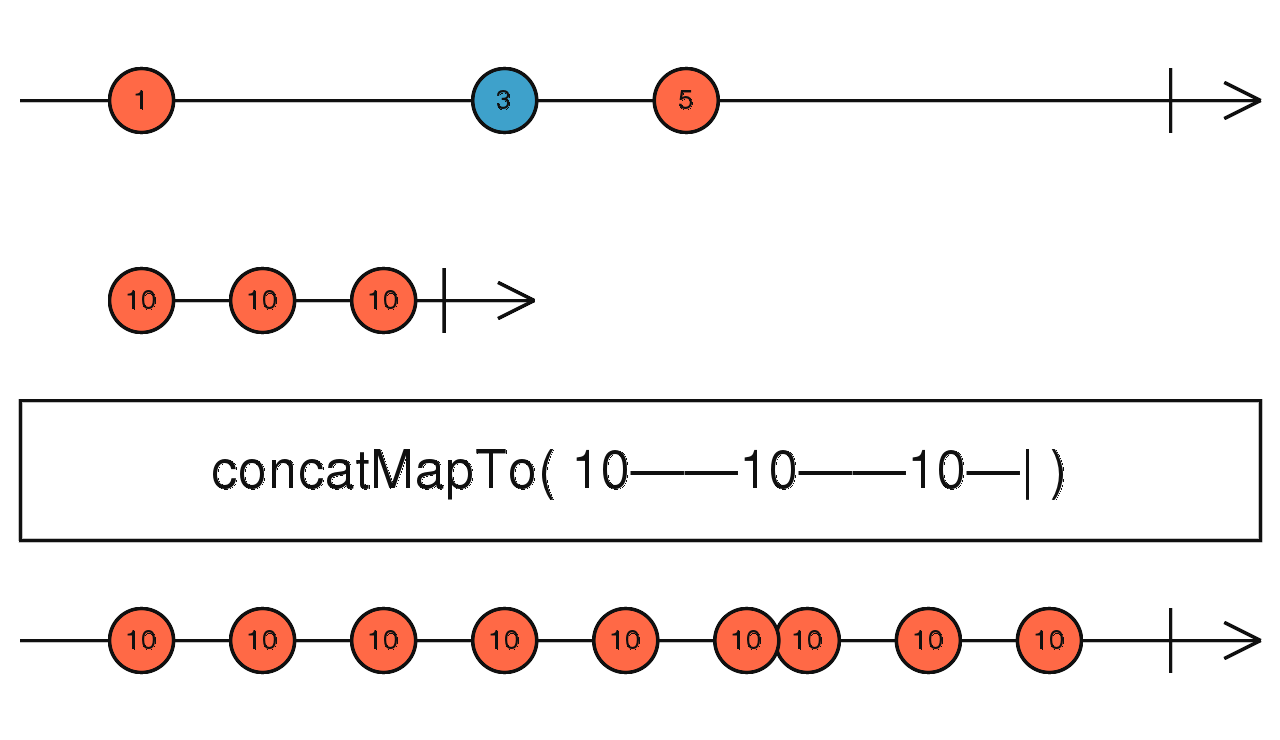
使用介面
concatMapTo(innerObservable: ObservableInput, resultSelector: function(outerValue: T, innerValue: I, outerIndex: number, innerIndex: number): any): Observable
使用範例
Observable.of(1,2,3,4,5)
.concatMapTo(
Observable.of('Hi'),
(outerValue, innerValue) => {
return innerValue + ' ' + outerValue;
})
.subscribe(value => console.log(value)); // 輸出: Hi 1, Hi 2, Hi 3, Hi 4, Hi 5
mergeMap
依資料發生的時序結合兩個 Observable 並做資料轉換
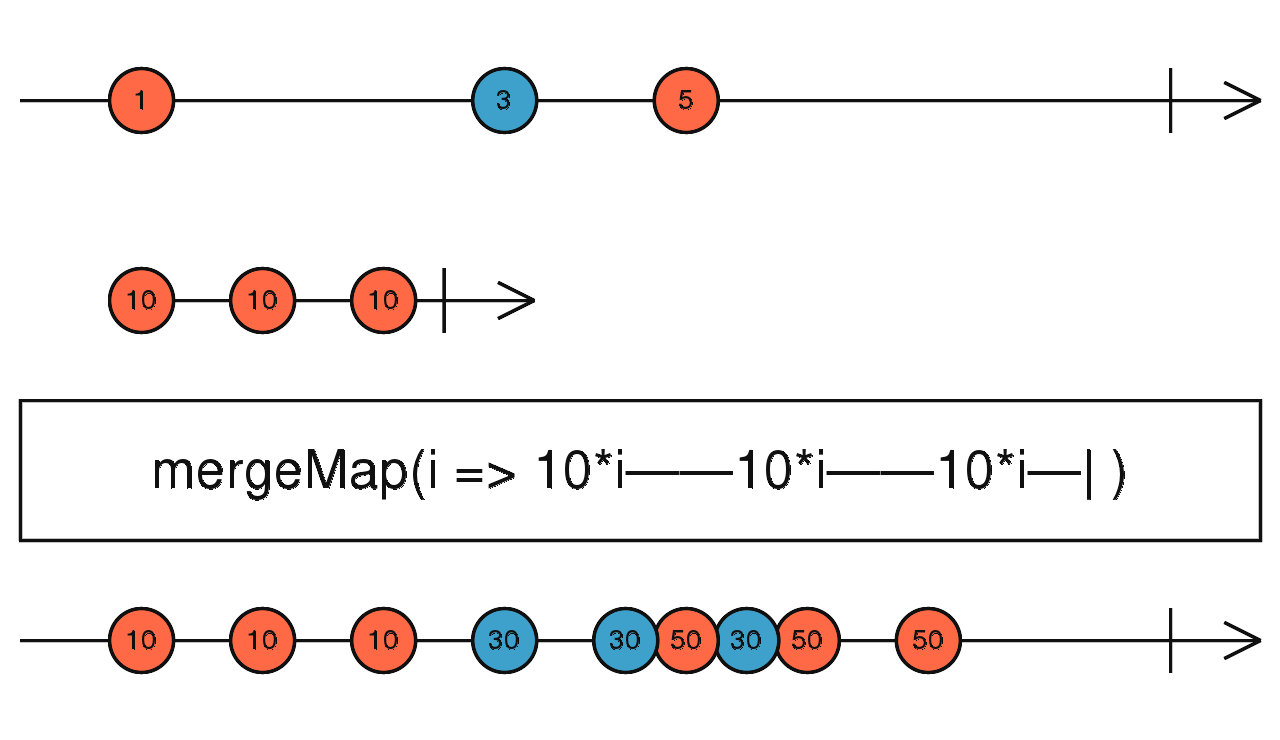
使用介面
mergeMap(project: function(value: T, ?index: number): ObservableInput, resultSelector: function(outerValue: T, innerValue: I, outerIndex: number, innerIndex: number): any, concurrent: number): Observable
使用範例
Observable.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
.mergeMap(
(value, idx) => {
const _v = value * (idx % 2 == 0 ? 1 : 2);
return Observable.of(_v);// 輸出:1, 4, 3, 8, 5
},
(outerValue, innerValue) => {
console.log({outerValue, innerValue}); // 輸出:{1,1},{2,4},{3,3},{4,8},{5,5}
return outerValue * innerValue
})
.subscribe(value => console.log(value));// 輸出:1, 8, 9, 32, 25
mergeMapTo
依資料發生的時序結合兩個 Observable 並送出一個固定的值
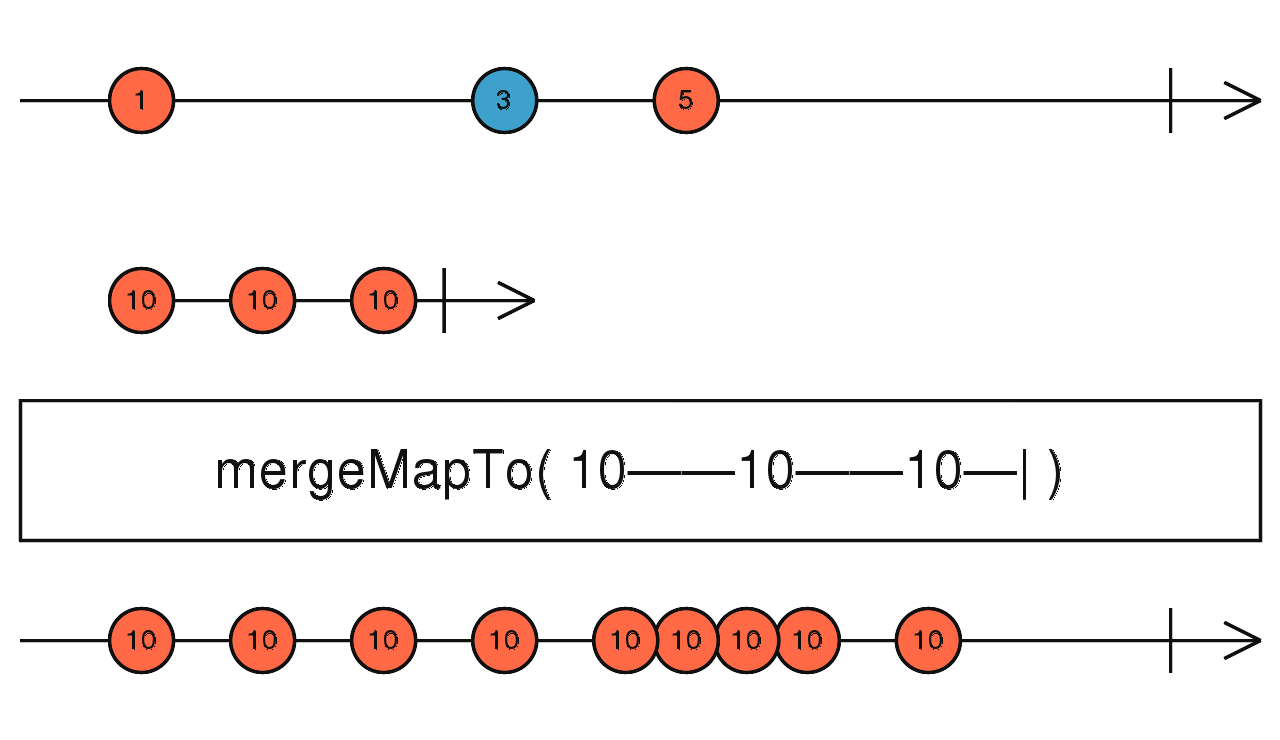
使用介面
mergeMapTo(innerObservable: ObservableInput, resultSelector: function(outerValue: T, innerValue: I, outerIndex: number, innerIndex: number): any, concurrent: number): Observable
使用範例
Observable.of(1,2,3,4,5)
.mergeMapTo(
Observable.of('Hi'),
(outerValue, innerValue) => {
return innerValue + ' ' + outerValue;
})
.subscribe(value => console.log(value)); // 輸出: Hi 1, Hi 2, Hi 3, Hi 4, Hi 5
switchMap
取最新發生的資料合併兩個 Observable 並做轉換
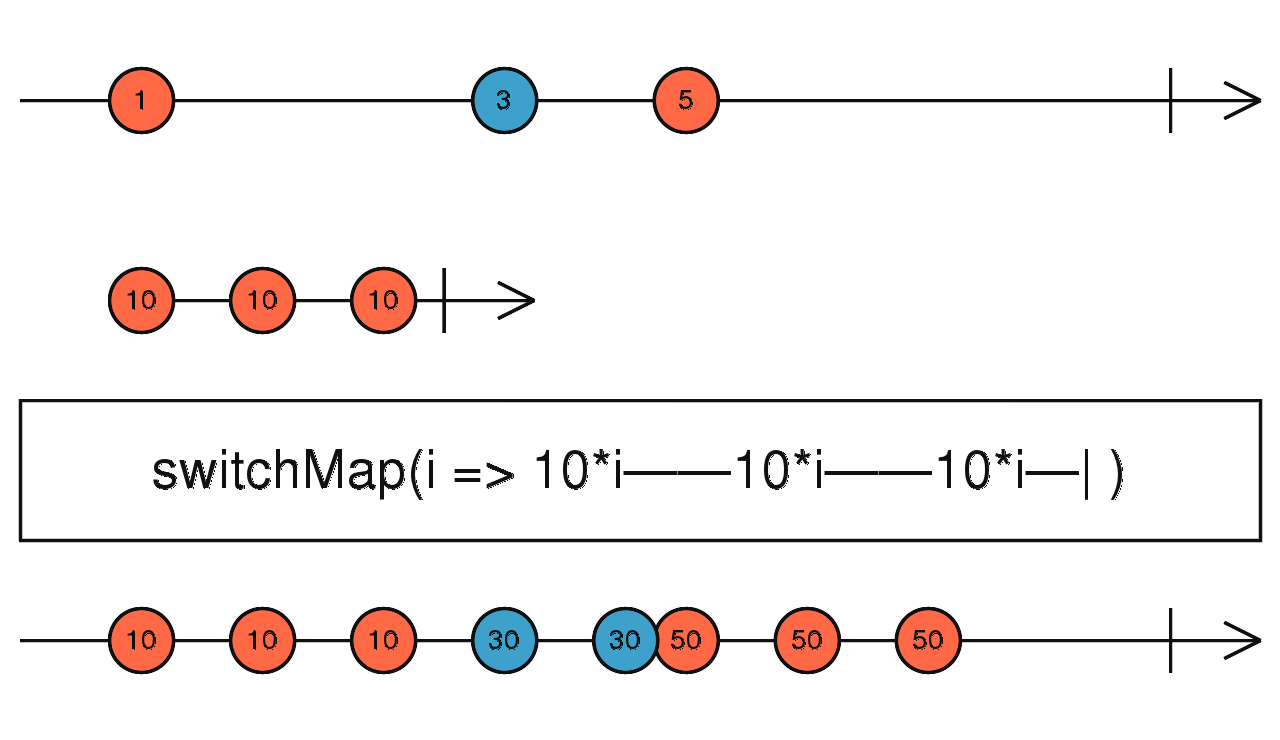
使用介面
switchMap(project: function(value: T, ?index: number): ObservableInput, resultSelector: function(outerValue: T, innerValue: I, outerIndex: number, innerIndex: number): any): Observable
使用範例
const clicks = Rx.Observable.fromEvent(document, 'click');
const result = clicks.switchMap((ev) => Rx.Observable.interval(1000));
result.subscribe(x => console.log(x));
在每一次 click 動作重新執行 Observable.interval 的動作
switchMapTo
就跟 switchMap 一樣,只是每次都回傳一樣的值
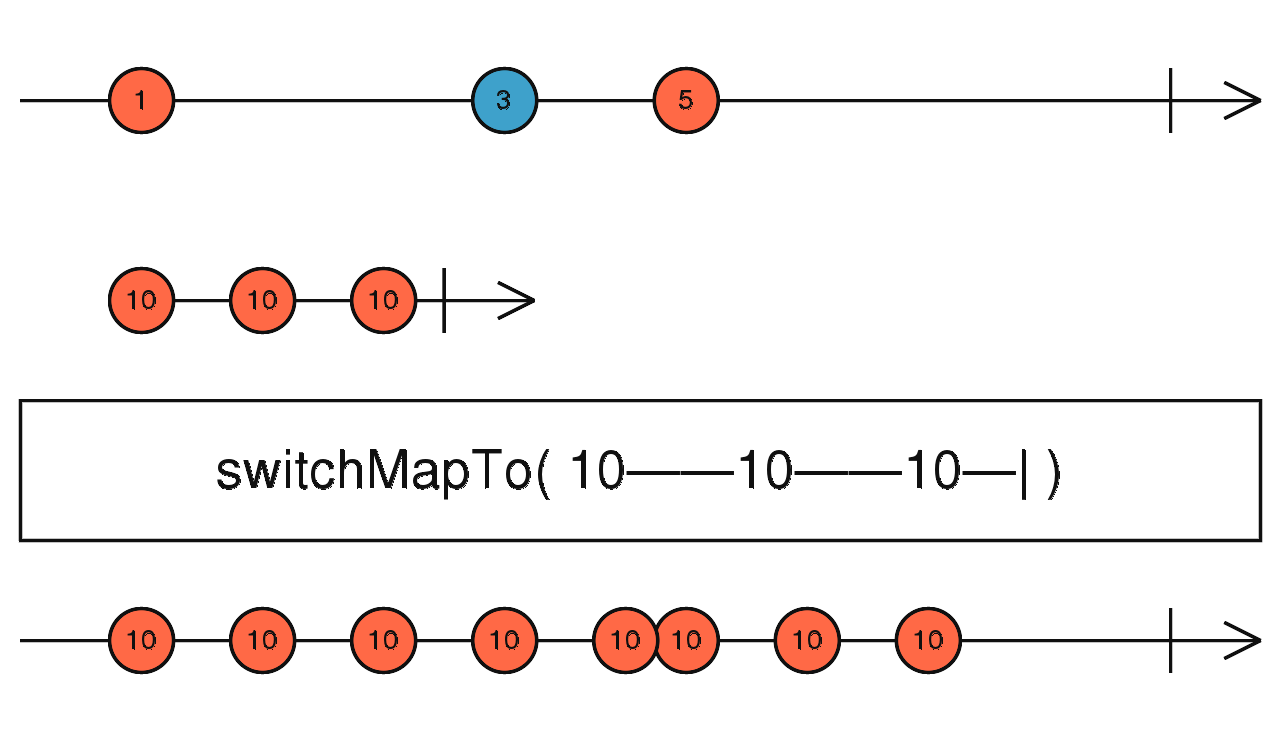
使用介面
switchMapTo(innerObservable: ObservableInput, resultSelector: function(outerValue: T, innerValue: I, outerIndex: number, innerIndex: number): any): Observable
使用範例
var clicks = Rx.Observable.fromEvent(document, 'click');
var result = clicks.switchMapTo(Rx.Observable.interval(1000));
result.subscribe(x => console.log(x));
exhaustMap
如果在上一個 Observable 動作未完成,又發生另一個 observable 動作,則這一個動作會被忽略。
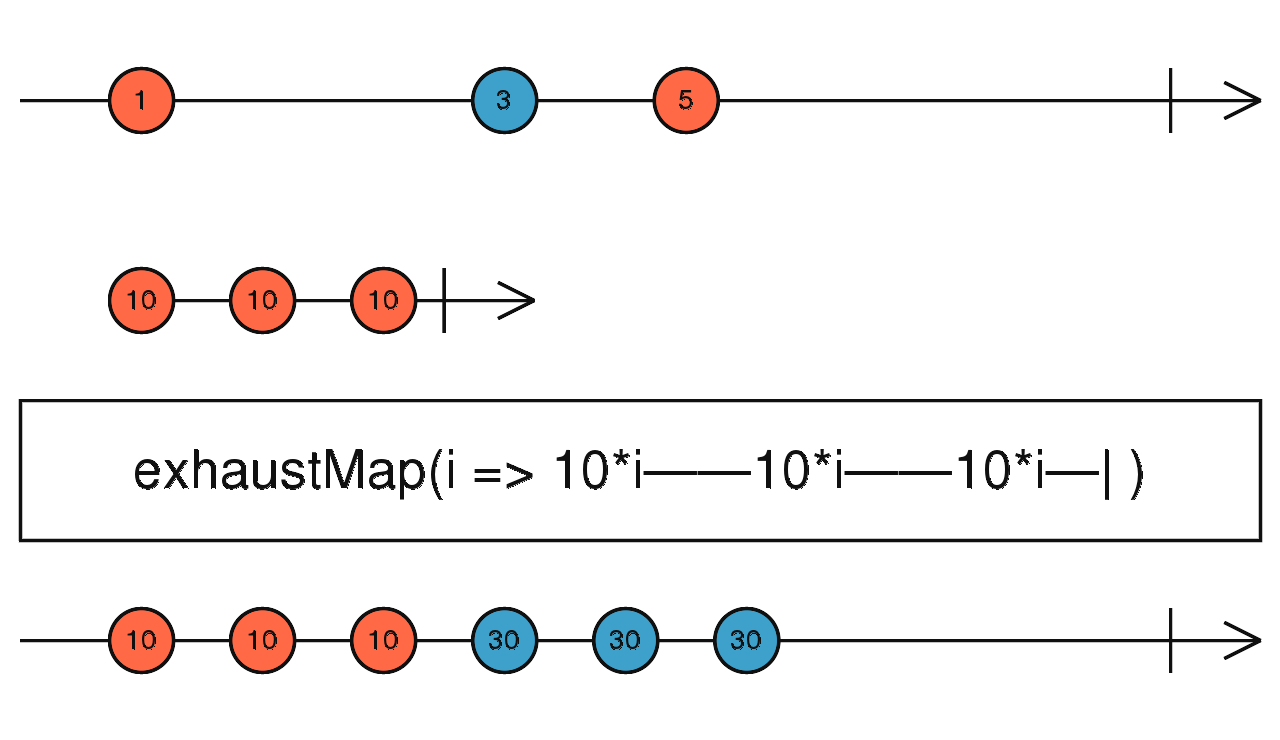
使用介面
exhaustMap(project: function(value: T, ?index: number): ObservableInput, resultSelector: function(outerValue: T, innerValue: I, outerIndex: number, innerIndex: number): any): Observable
使用範例
var clicks = Rx.Observable.fromEvent(document, 'click');
var result = clicks.exhaustMap(Rx.Observable.interval(1000));
result.subscribe(x => console.log(x));
expand
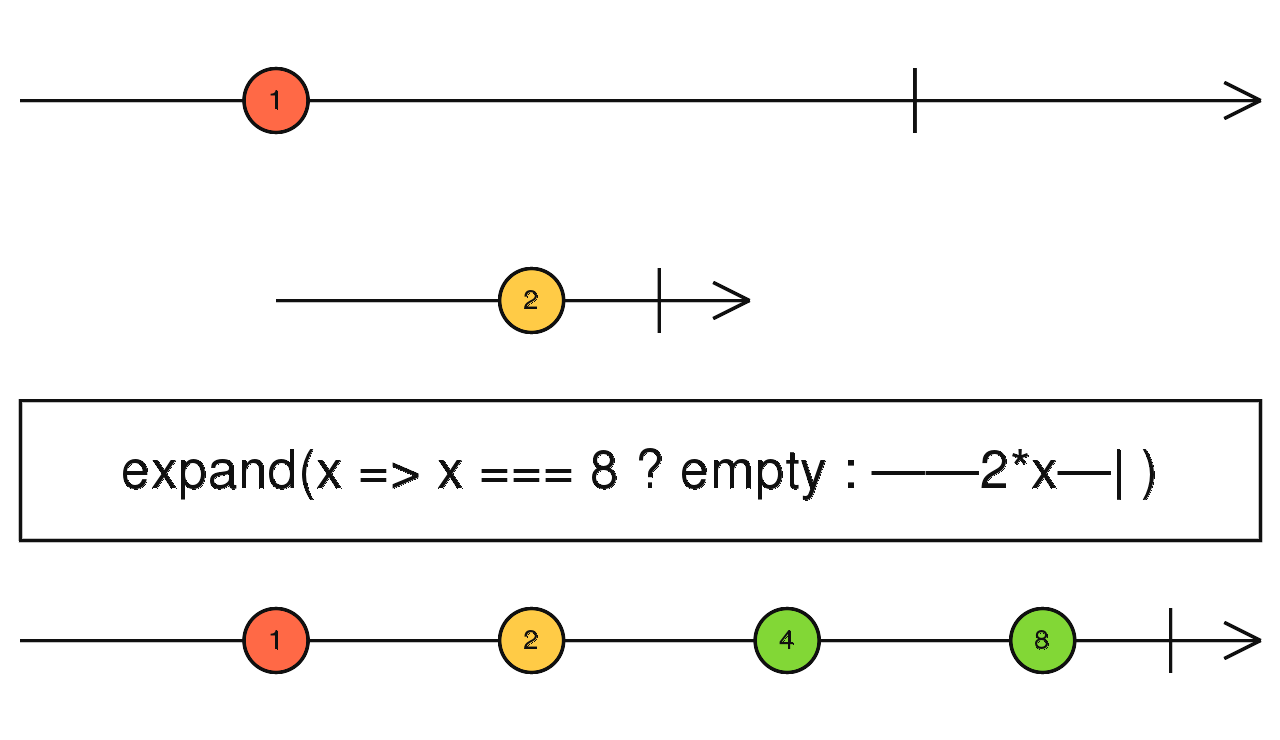
使用介面
expand(project: function(value: T, index: number), concurrent: number, scheduler: Scheduler): Observable
使用範例
Observable.of(1, 2)
.expand((value: number) => {
if (value === 8)
return Observable.empty();
else
return Observable.of(value * 2);
})
.subscribe(x => console.log(x)); // 輸出 1, 2, 4, 8, 2, 4, 8
groupBy
根據條件將資料群組化輸出成獨立的 Observable
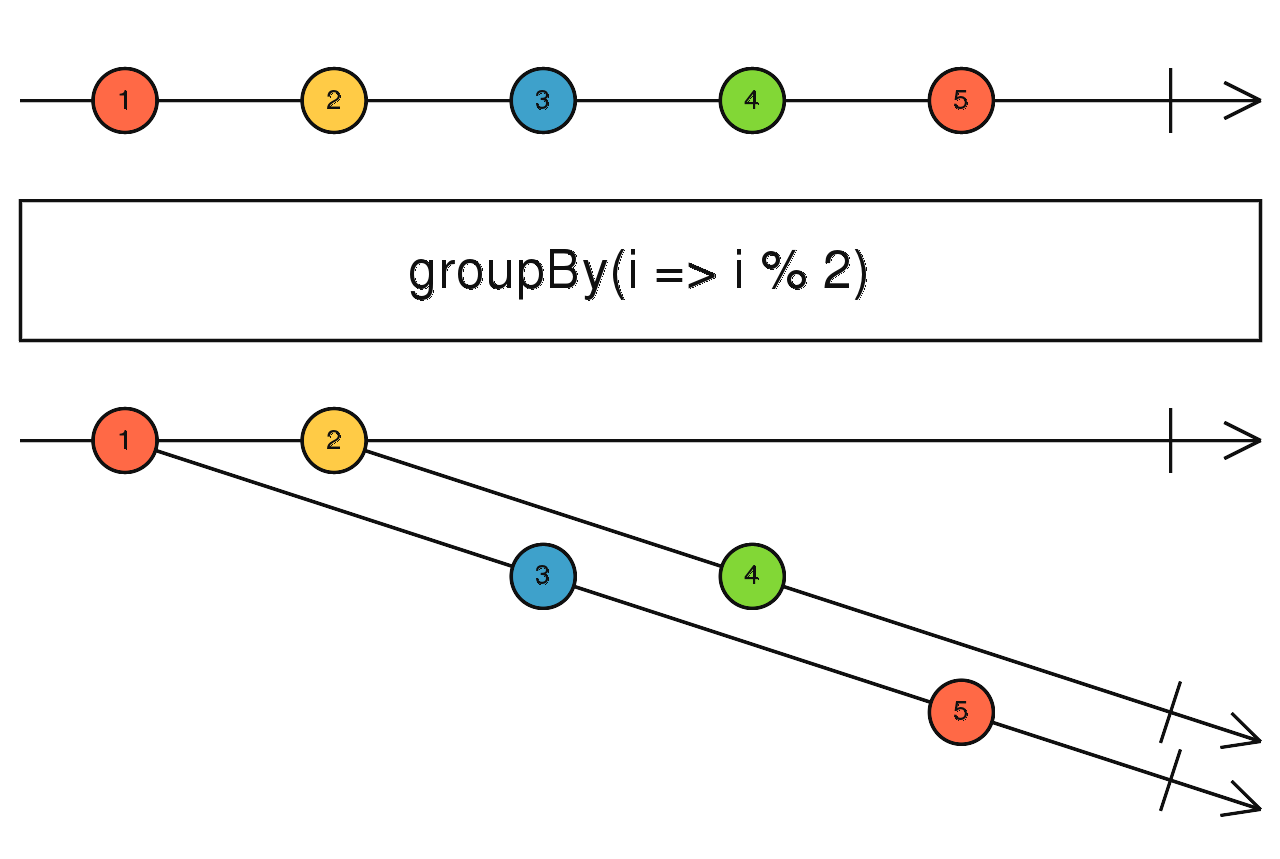
使用介面
GroupBy(keySelector: function(value: T): K, elementSelector: function(value: T): R, durationSelector: function(grouped: GroupedObservable<K, R>): Observable<any>): Observable<GroupedObservable<K, R>>
使用範例
const data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let groupData = [];
Observable.from(data).groupBy(x => x % 2, (ele)=> ele + '!').subscribe(g => {
let group = {key: g.key, values: []};
g.subscribe(value => {
group.values.push(value);
});
groupData.push(group);
});
if (groupData) {
console.log(groupData); // 輸出: [{key: 1, values: [1!, 3!, 5!]}, {key: 2, values: [2!, 4!]}]
}
const data = [
{currency: 'USD', amount: 100}, {currency: 'NTD', amount: 100},
{currency: 'USD', amount: 150}, {currency: 'HKD', amount: 200}
];
function groupData() {
Observable.from(data)
.groupBy(x => x.currency)
.mergeMap(
group => group.reduce(
(acc, item) => {
acc.key = acc.key || group.key;
acc.items = [...acc.items, item];
return acc;
},
{key: '', items: []}))
.map(item => {
const total = item.items.reduce((acc, item) => acc + item.amount, 0);
return {key: item.key, items: item.items, total: total};
})
.toArray()
.subscribe(value => {
console.log(value);
/* 輸出結果
[ { key: 'USD', items: [{currency: 'USD', amount: 100},
{currency: 'USD', amount: 150}], total: 250 },
{ key: 'NTD', items: [{currency: 'NTD', amount: 100}],total: 100 },
{ key: 'HKD', items: [{currency: 'HKD', amount: 200}], total: 200 } ]
*/
});
}
groupData();
// 使用多個 groupBy key 值的寫法
const people = [{ name: 'Sue', age: 25 }, { name: 'Sue', age: 25 }, { name: 'Joe', age: 30 }, { name: 'Sarah', age: 35 }];
const source = Observable.from(people);
const example = source
.groupBy(p => JSON.stringify({ age: p.age, name: p.name }))
.flatMap(group => group.reduce((acc, curr) => [...acc, curr], []));
const subscribe = example.subscribe(val => console.log(val));
// [ { name: 'Sue', age: 25 }, { name: 'Sue', age: 25 } ]
// [ { name: 'Joe', age: 30 } ]
// [ { name: 'Sarah', age: 35 } ]
mergeScan
執行 scan 動作時,會回傳一個 observable 並與 outer observable 做 merge
使用介面
mergeScan(accumulator: function(acc: R, value: T): Observable<R>, seed: *, concurrent: number): Observable<R>
使用範例
const data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
Observable.from(data)
.mergeScan((acc, one) => Observable.of(acc + one), 0)
.subscribe(value => console.log(value)); // 輸出: 1, 3, 6, 10, 15
pairwise
將前一次與本次發生的資料合併輸出
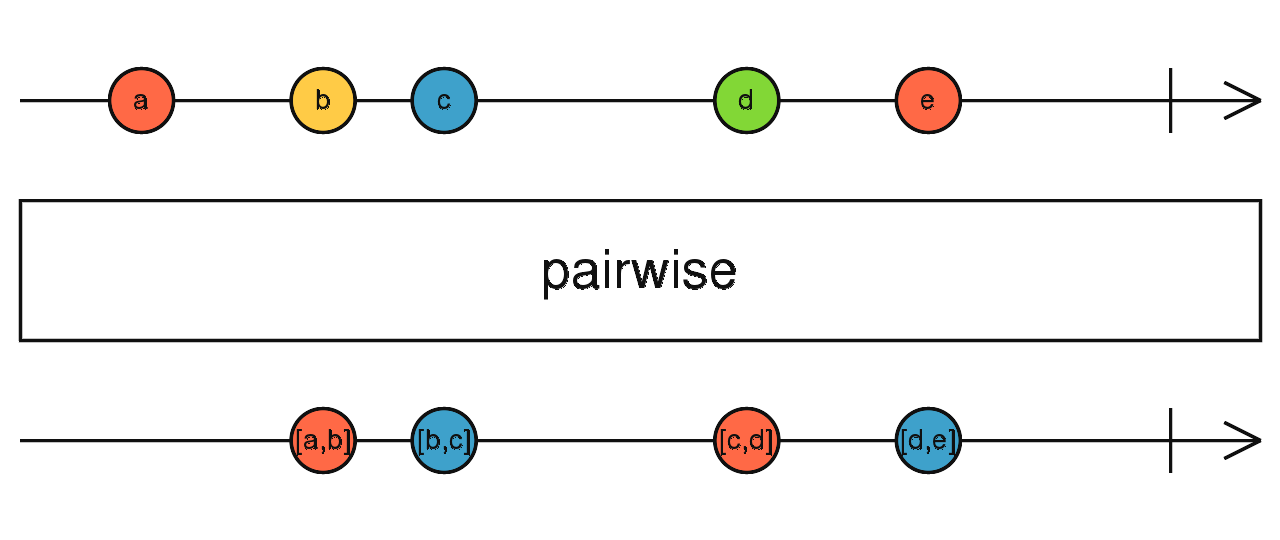
使用介面
pairwise(): Observable<Array<T>>
使用範例
const data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
Observable.from(data)
.pairwise()
.subscribe(value => {
console.log(value); // 輸出: [1,2], [2,3], [3,4], [4,5]
});
partition
根據條件分成符合與不符合條件的兩組 Observable
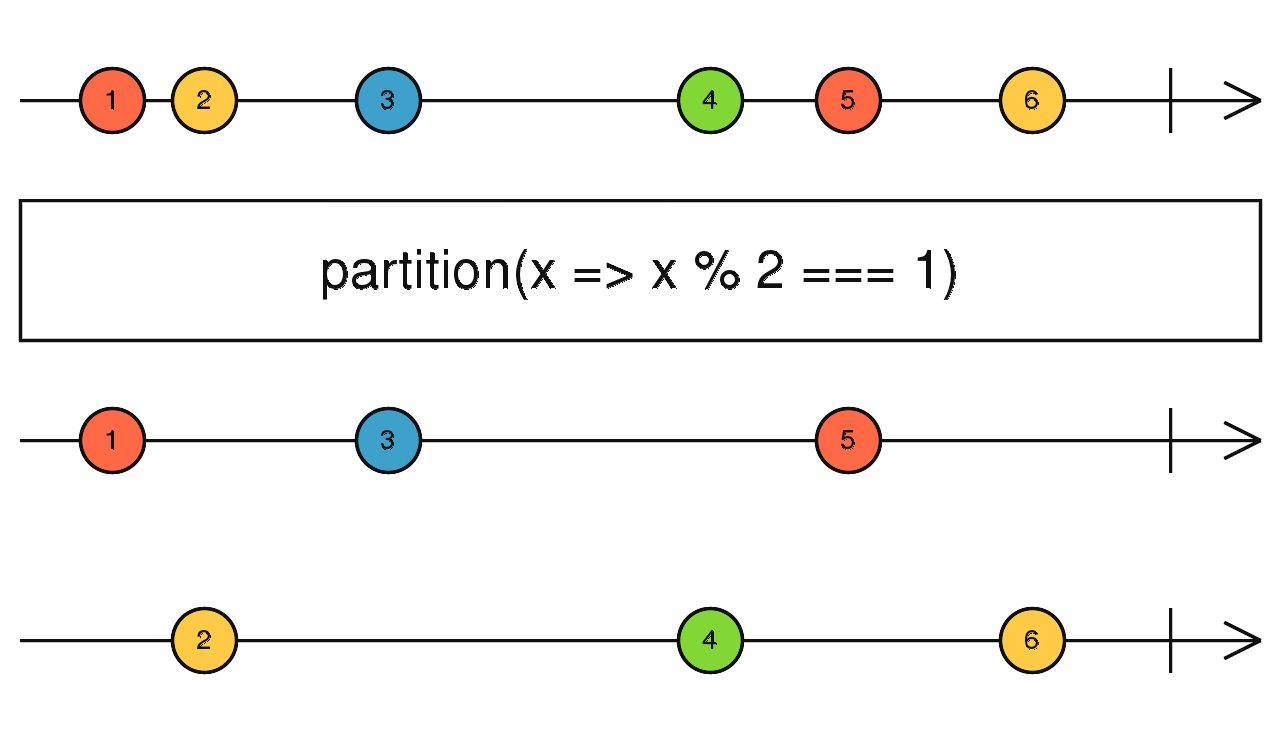
使用介面
partition(predicate: function(value: T, index: number): boolean, thisArg: any): [Observable<T>, Observable<T>]
使用範例
const data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let parts = Observable.from(data).partition(x => x % 2 === 1);
parts[0].subscribe(value => {
console.log(value); // 輸出: 1, 3, 5
});
parts[1].subscribe(value => {
console.log(value); // 輸出: 2, 4
});
pluck
取出特定的屬性,可以透過第二,及第三引數等,取得更深層的屬性
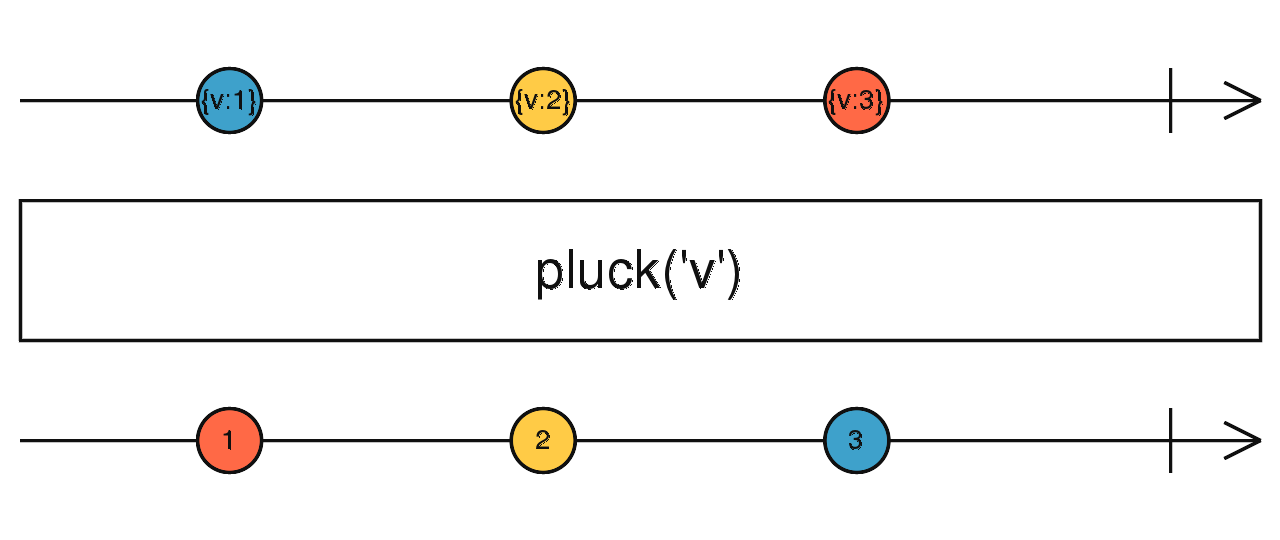
使用介面
pluck(properties: ...string): Observable
使用範例
import 'rxjs';
import {Observable} from 'rxjs/Observable';
const data = [{name: 'a', sex: 1}, {name: 'b', sex: 1}, {name: 'c', sex: 0}]
Observable.from(data)
.pluck('name')
.subscribe(value => console.log(value)); // 輸出: a, b, c
import 'rxjs';
import {Observable} from 'rxjs/Observable';
const data = [
{
id: 1,
company: {
name: 'Romaguera-Crona',
catchPhrase: 'Multi-layered client-server neural-net',
bs: 'harness real-time e-markets'
}
},
{
id: 2,
company: {
name: 'Deckow-Crist',
catchPhrase: 'Proactive didactic contingency',
bs: 'synergize scalable supply-chains'
}
},
{
id: 3,
company: {
name: 'Romaguera-Jacobson',
catchPhrase: 'Face to face bifurcated interface',
bs: 'e-enable strategic applications'
}
}
];
Observable.from(data)
.pluck('company', 'name')
.subscribe(value => {
console.log(value); // 輸出: Romaguera-Crona, Deckow-Crist, Romaguera-Jacobson
});
scan
類似 JavaScript 的 reduce,每次都會輸出計算後的值,且保留之前的狀態
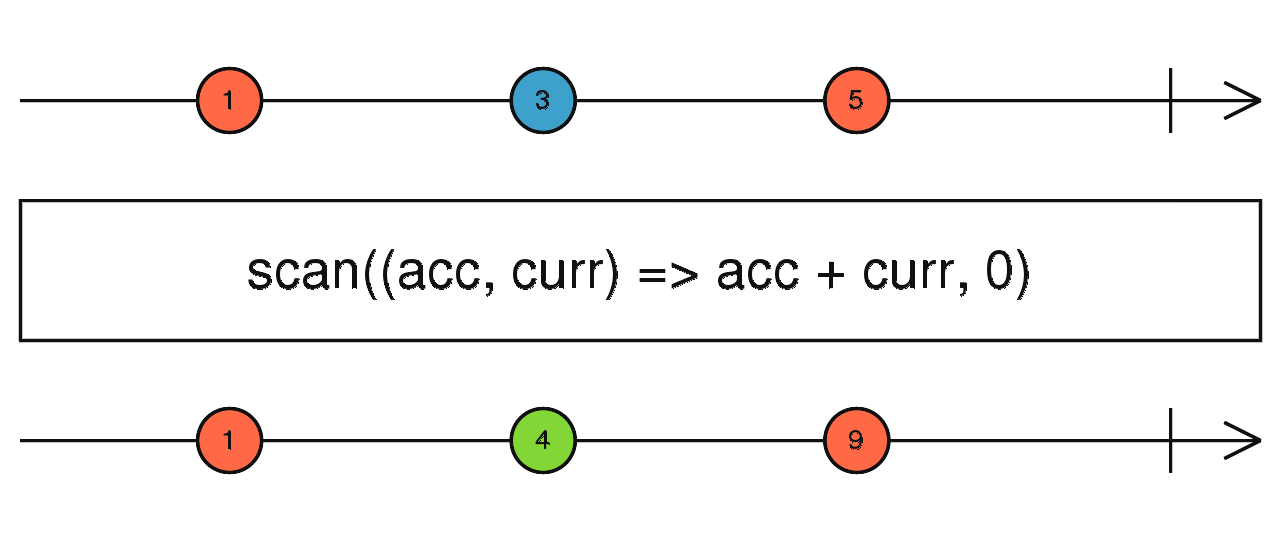
使用介面
scan(accumulator: function(acc: R, value: T, index: number): R, seed: T | R): Observable<R>
使用範例
const subScan = new Subject();
subScan.scan((acc: number, one: number) => acc + one, 0)
.subscribe(value => console.log(value));
subScan.next(1); // 輸出: 1
subScan.next(1); // 輸出: 2
buffer
根據 Observable 條件決定緩衝空間,當緩衝空間滿時,則輸出資料
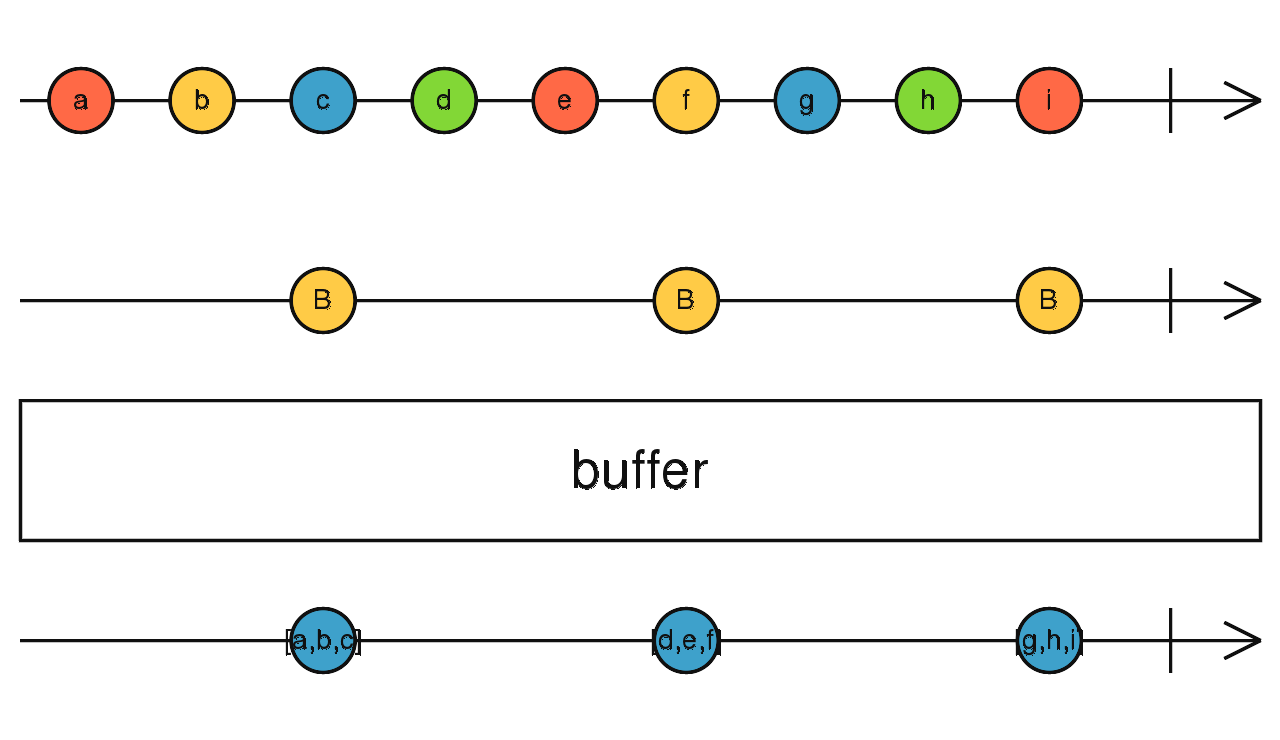
使用介面
buffer(closingNotifier: Observable<any>): Observable<T[]>
使用範例
Observable.interval(250)
.take(10)
.buffer(Observable.interval(1000))
.subscribe(value => console.log(value)); // 輸出:[0,1,2], [3,4,5,6]
bufferCount
根據資料數量條件決定緩衝空間,當緩衝空間滿時,則輸出資料
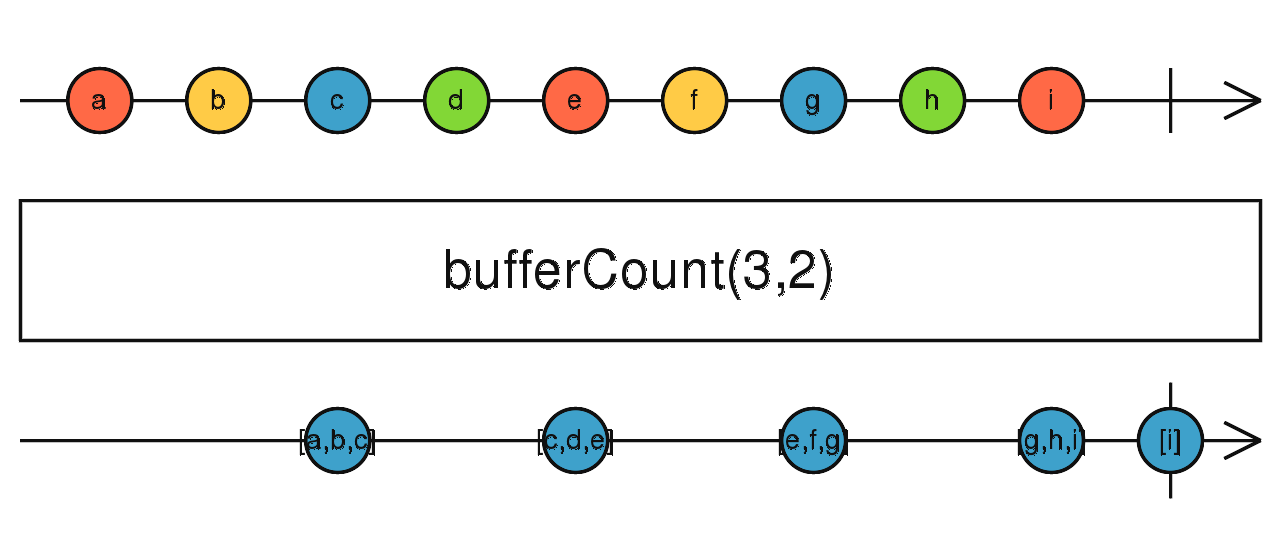
使用介面
bufferCount(bufferSize: number, startBufferEvery: number): Observable<T[]>
使用範例
Observable.interval(300)
.take(10)
.bufferCount(3)
.subscribe(value => console.log(value)); // 輸出: [0,1,2], [3,4,5],[6,7,8],[9]
Observable.interval(300)
.take(10)
.bufferCount(3,2)
.subscribe(value => console.log(value)); // 輸出: [0,1,2], [2,3,4],[4,5,6],[6,7,8].[8,9]
bufferTime
根據時間條件決定緩衝空間,當緩衝空間滿時,則輸出資料
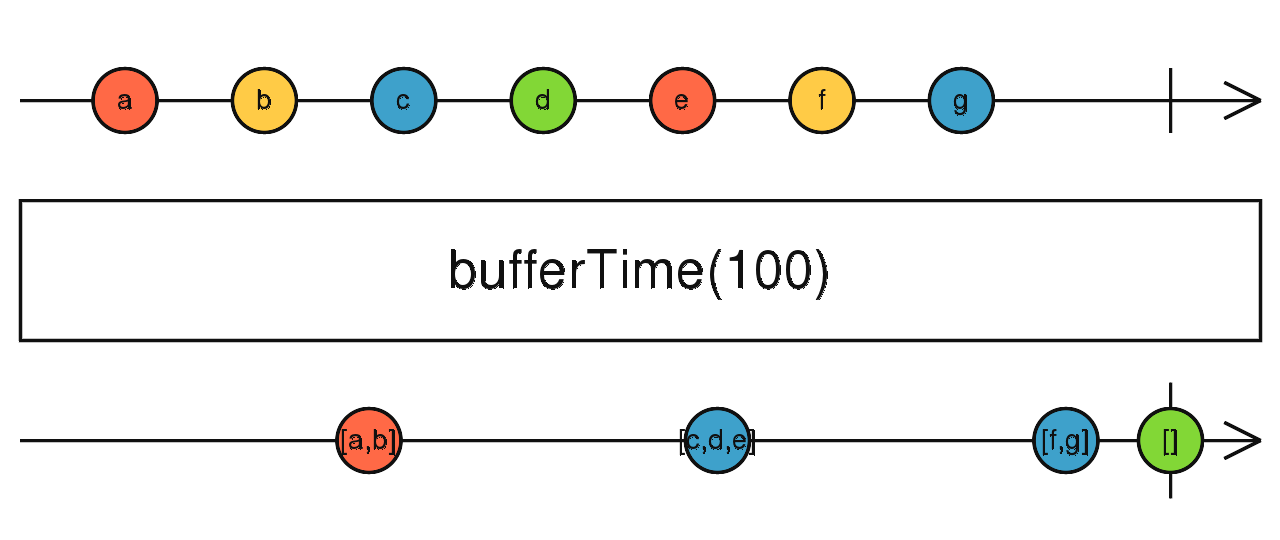
使用介面
bufferTime(bufferTimeSpan: number, bufferCreationInterval: number, maxBufferSize: number, scheduler: Scheduler): Observable<T[]>
使用範例
Observable.interval(300)
.take(10)
.bufferTime(1000)
.subscribe(value => console.log(value));
bufferToggle
根據開始與結束開關決定緩衝空間,當緩衝空間滿時,則輸出資料
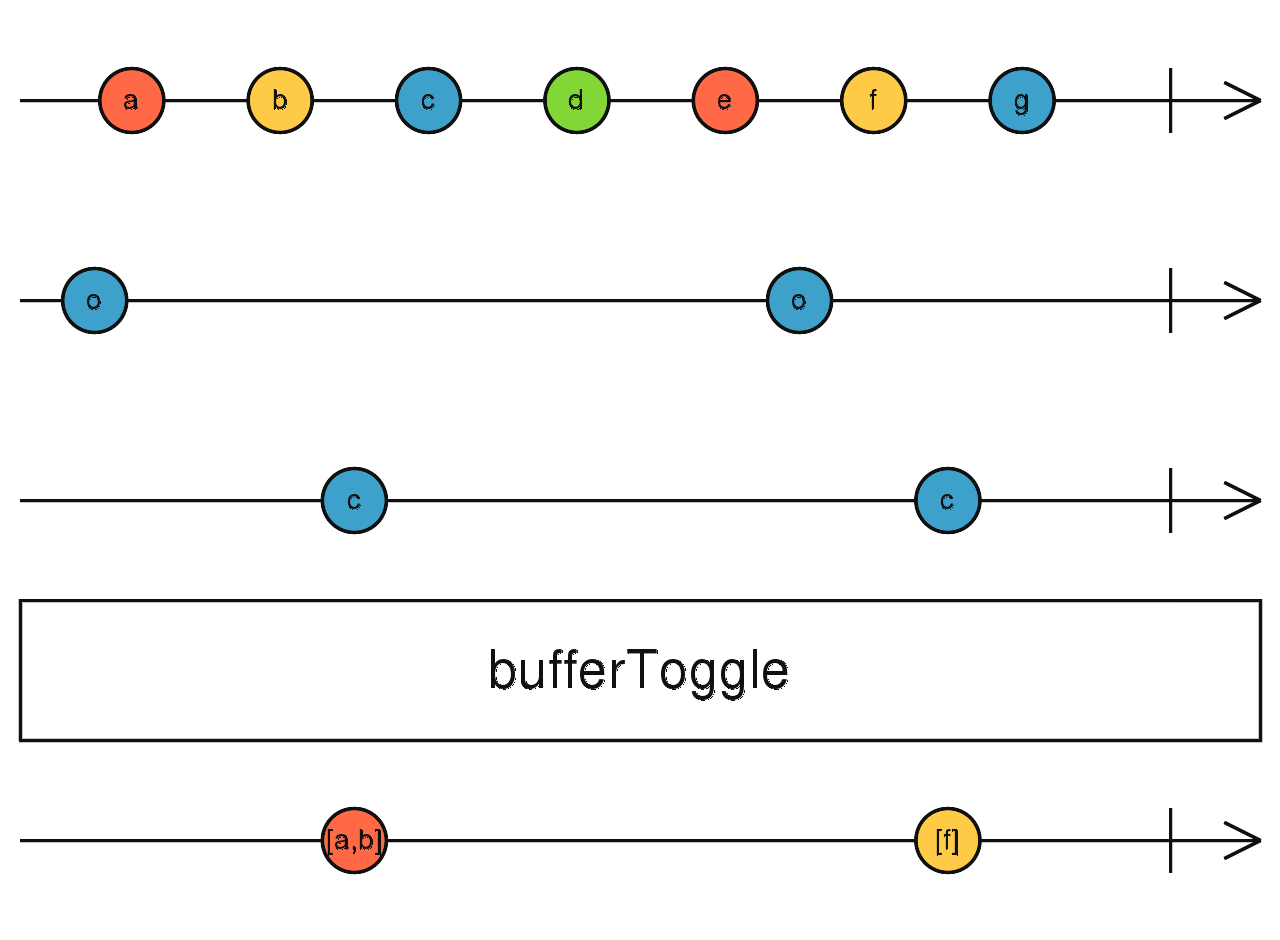
使用介面
bufferToggle(openings: SubscribableOrPromise<O>, closingSelector: function(value: O): SubscribableOrPromise): Observable<T[]>
使用範例
// 0123456789
// oc oc
Observable.interval(250)
.take(10)
.bufferToggle(Observable.interval(1000), x => Observable.interval(500))
.subscribe(value => console.log(value)); // 輸出: [3,4],[7,8]
bufferWhen
根據結束開關決定緩衝空間,當緩衝空間滿時,則輸出資料
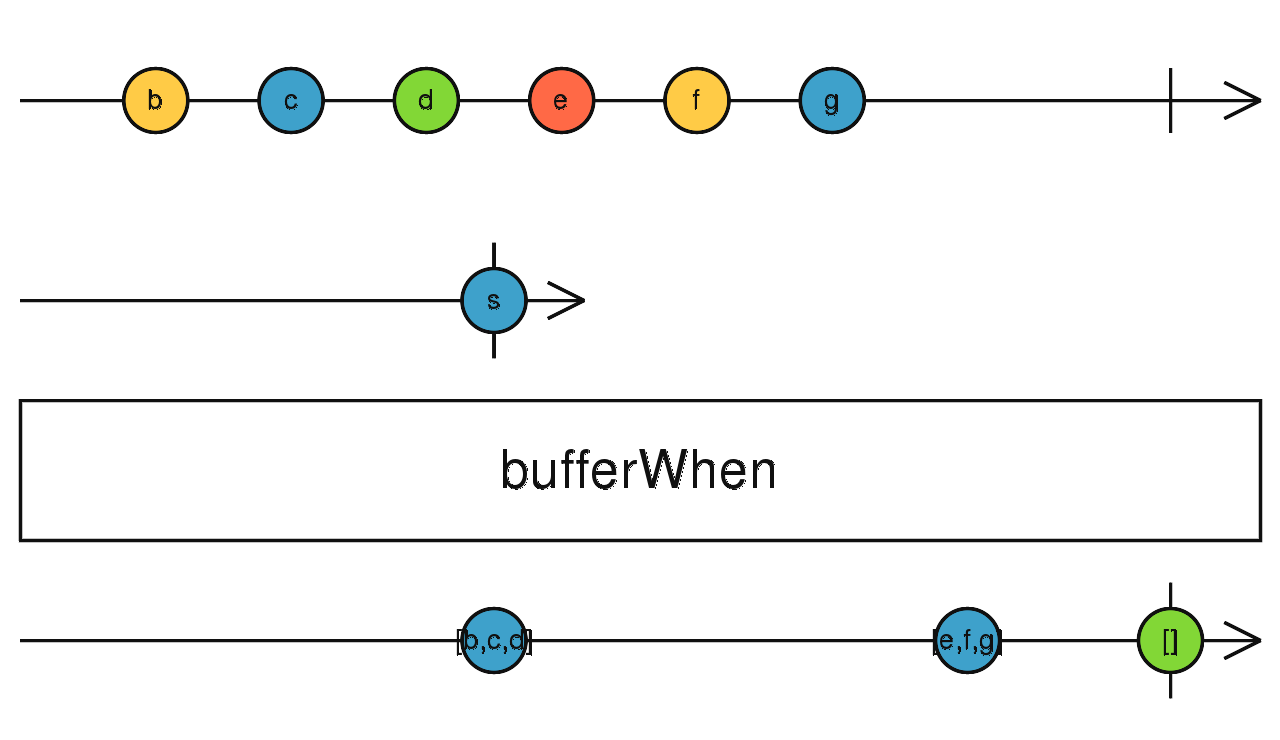
使用介面
bufferWhen(closingSelector: function(): Observable): Observable<T[]>
使用範例
Observable.interval(250)
.take(10)
.bufferWhen(() => Observable.interval(1000))
.subscribe(value => console.log(value)); // 輸出:[0,1,2],[3,4,5,6],[7,8,9]
window
根據 Observable 條件決定緩衝空間,當緩衝空間滿時,則輸出包含緩衝資料的新Observable

使用介面
window(windowBoundaries: Observable<any>): Observable<Observable<T>>
使用範例
let i = 0;
let groupsData = [];
Observable.interval(250)
.take(10)
.window(Observable.interval(1000))
.subscribe(value => {
let group = {groupId: ++i, values: []};
value.forEach(v => group.values.push(v));
groupsData.push(group);
});
windowCount
根據資料數量條件決定緩衝空間,當緩衝空間滿時,輸出包含緩衝資料的新Observable
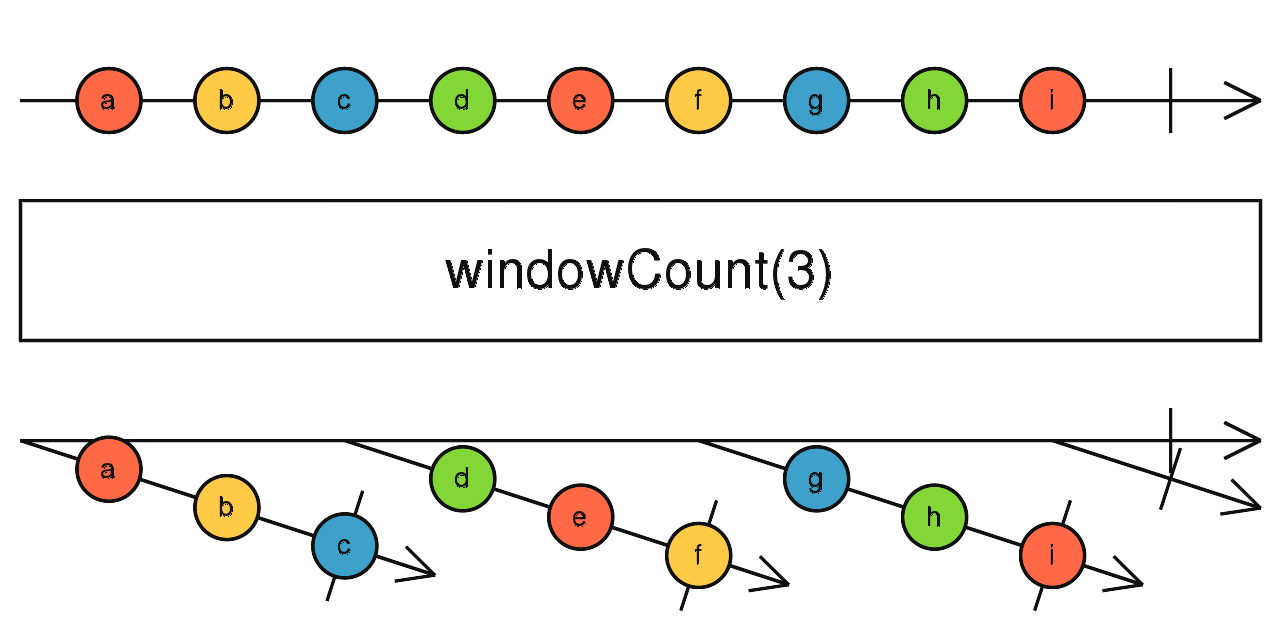
使用介面
windowCount(windowSize: number, startWindowEvery: number): Observable<Observable<T>>
使用範例
let i = 0;
let groupsData = [];
Observable.interval(250)
.take(10)
.windowCount(3)
.subscribe(value => {
let group = {groupId: ++i, values: []};
value.forEach(v => group.values.push(v));
groupsData.push(group);
});
windowTime
根據時間條件決定緩衝空間,當緩衝空間滿時,輸出包含緩衝資料的新Observable
使用介面
windowTime(bufferTimeSpan: number, bufferCreationInterval: number, maxBufferSize: number, scheduler: Scheduler): Observable<Observable<T>>
使用範例
let i = 0;
let groupsData = [];
Observable.interval(250)
.take(10)
.windowTime(1000)
.subscribe(value => {
let group = {groupId: ++i, values: []};
value.forEach(v => group.values.push(v));
groupsData.push(group);
console.log(groupsData);
});
windowToggle
根據開始與結束開關決定緩衝空間,當緩衝空間滿時,輸出包含緩衝資料的新Observable
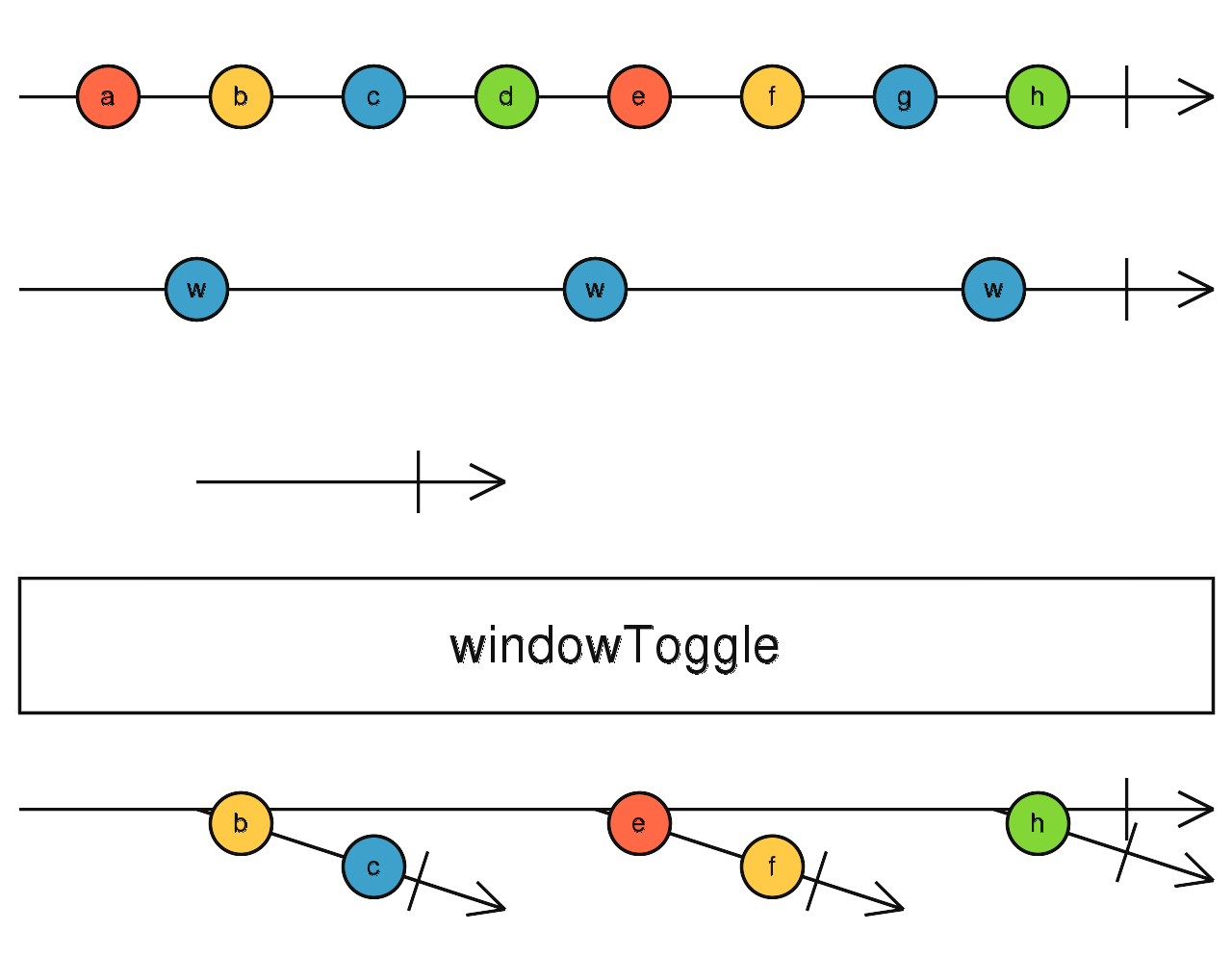
使用介面
windowToggle(openings: Observable<O>, closingSelector: function(value: O): Observable): Observable<Observable<T>>
使用範例
let i = 0;
let groupsData = [];
Observable.interval(250)
.take(10)
.windowToggle(Observable.interval(1000), x => Observable.interval(500))
.subscribe(value => {
let group = {groupId: ++i, values: []};
value.forEach(v => group.values.push(v));
groupsData.push(group);
console.log(groupsData);
});
windowWhen
根據結束開關決定緩衝空間,當緩衝空間滿時,輸出包含緩衝資料的新Observable
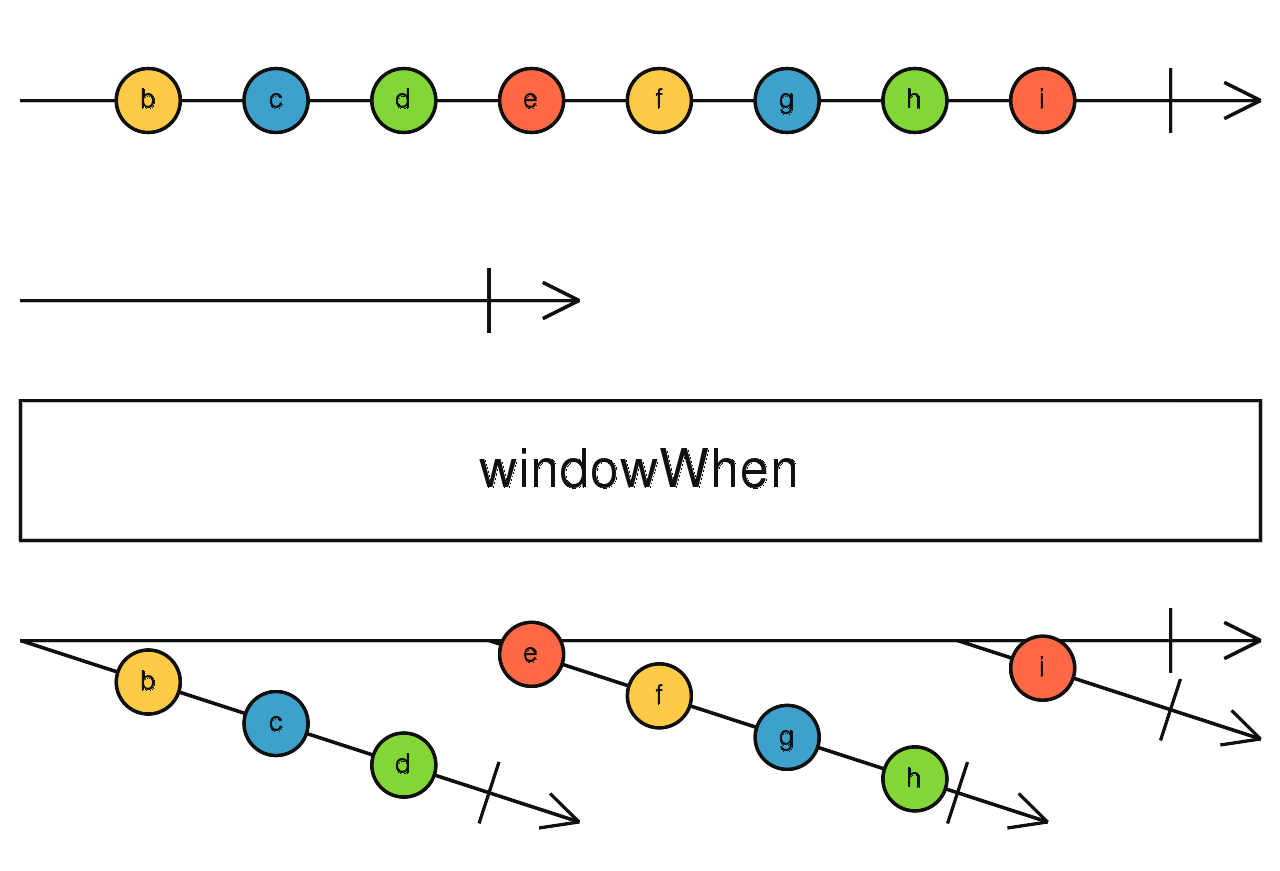
使用介面
windowWhen(closingSelector: function(): Observable): Observable<Observable<T>>
使用範例
let i = 0;
let groupsData = [];
Observable.interval(250)
.take(10)
.windowWhen(()=> Observable.interval(1000))
.subscribe(value => {
let group = {groupId: ++i, values: []};
value.forEach(v => group.values.push(v));
groupsData.push(group);
console.log(groupsData);
});